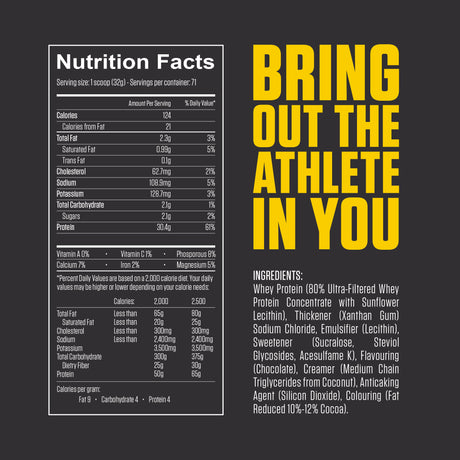
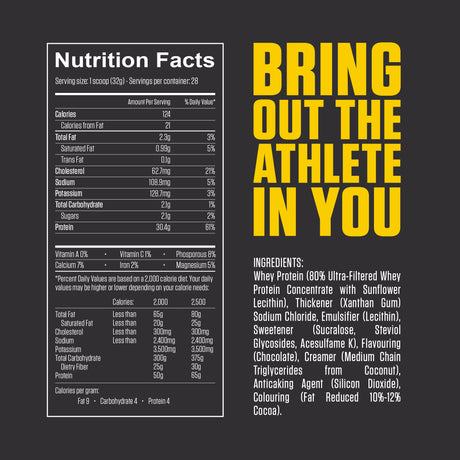
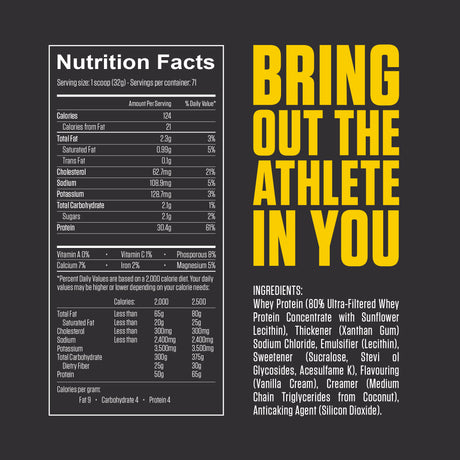
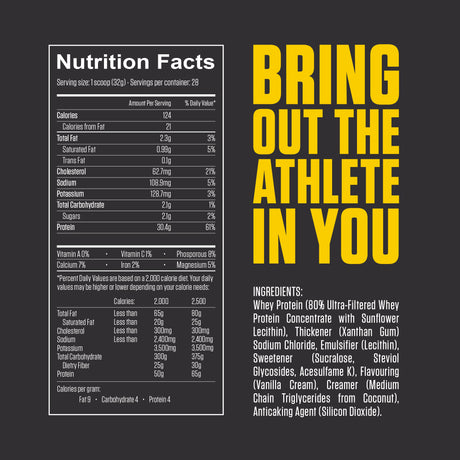
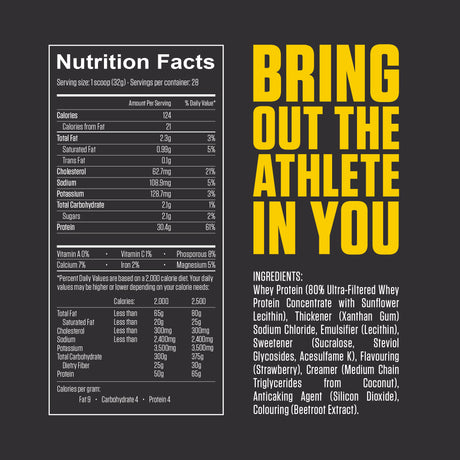
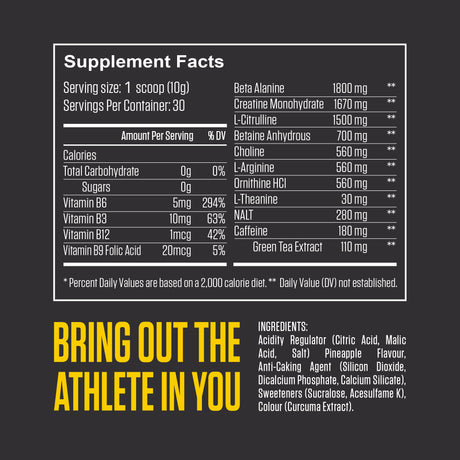
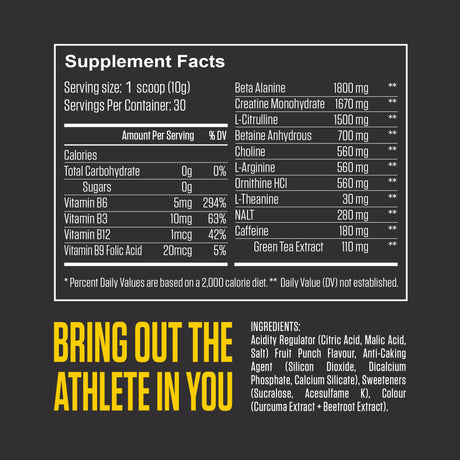
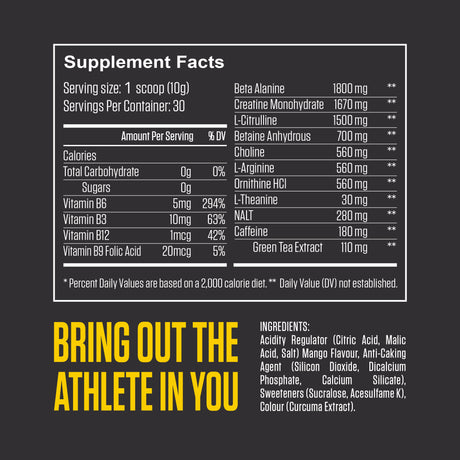
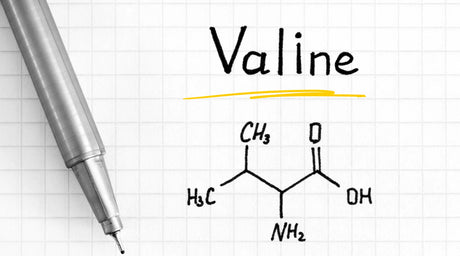
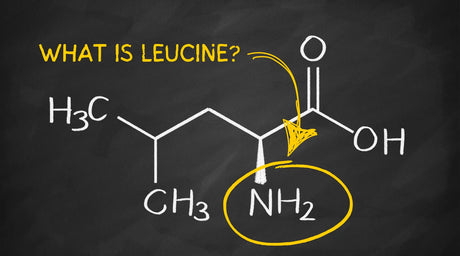
Leucine is one of the nine essential amino acids, meaning the body cannot produce it and must obtain it through diet or supplements. It is a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), along with isoleucine and valine. Leucine is particularly well-known for its vital role in muscle protein synthesis, making it important for muscle growth, repair, and recovery.
Key Roles of Leucine:
Stimulates Muscle Protein Synthesis
Leucine is the most potent BCAA for triggering muscle protein synthesis, a process that leads to muscle growth and recovery. It activates the mTOR pathway, which is a key regulator of cell growth and muscle protein production.
Prevents Muscle Breakdown
Leucine helps to maintain muscle mass by preventing muscle catabolism, particularly during periods of stress, such as intense exercise or calorie restriction. It provides an energy source for muscles, reducing the need for the body to break down its own muscle tissue.
Supports Recovery
By enhancing muscle repair and reducing muscle damage post-exercise, leucine helps speed up recovery, reducing muscle soreness and improving overall workout performance.
Balances Blood Sugar Levels
Leucine can influence insulin release, helping to regulate blood sugar levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into muscle cells, where it can be used as energy.
Dietary Sources of Leucine:
Leucine is found in many protein-rich foods, especially animal products. Some good sources include:
- Meat, poultry, and fish
- Eggs
- Dairy products like cheese and milk
- Soybeans and legumes
- Nuts and seeds
Due to its critical role in muscle metabolism, leucine is often included in BCAA supplements or other protein supplements aimed at supporting muscle growth and recovery.